We are looking at a 2023 study relative to Alzheimer’s where actual Alzheimer’s patients were given an aloe-Acemannan nutritional supplement over a 12 month period of time. The authors, as far as they know, are saying this is the first study that has closely measured an immune ratio in Alzheimer’s patients, and compared it to healthy people. Let’s dig in further.
The name of this study. The Characterization of the Th1/Th2 Ratio in Moderate-Severe Alzheimer’s Disease Patients and Its Response to an Aloe Polymannose-Based Dietary Supplement. According to the authors of this research, no one had really studied the balance between Th1 and Th2 in Alzheimer’s patients before this study. (This is reference to what is called the Th1/Th2 ratio. In simplest of terms Th1 and Th2 are two different “types” of immune responses. Th1 is more pro-inflammatory (it fights infections when and where needed, but too much can hurt the brain), and Th2 is more anti-inflammatory (helps calm things down and if it doesn’t respond appropriately then inflammation can turn chronic). The researchers measured this Th1/Th2 balance using cytokines. Cytokines are chemical messengers of the immune system, such as: IL-2 (Interleukin 2), IL-10 (Interleukin 10), IFN-γ (Interferon gamma), IL-4 (Interleukin 4), TNF-α (Tumor necrosis factor alpha)
The ratios between these cytokines (e.g., IL-2/IL-10 represents a ratio) tell researchers whether the immune system is leaning more toward inflammation (Th1) or leaning toward calming down the inflammation(Th2). Cytokines have many roles depending on the type. Some are pro-inflammatory, some anti-inflammatory, and some regulatory, like a thermostat. In other words, They don’t “heat” or “cool” like Th1 or Th2 cytokines — instead, they sense the environment and adjust the settings to keep everything in a safe range.
For clarity’s sake: The forward slash (/) in each ratio acts like a math fraction: the first number is divided by the second number. The number on top is the numerator, and the one on the bottom is the denominator.
Imagine this like a balanced scale:
If the numerator (Th1) is heavier, the scale tips toward inflammation.
If the denominator (Th2) is heavier, it tips toward anti-inflammation.
When both sides are equal, the scale is balanced — showing immune harmony. Or what scientists refer to as unity.
For example:
Th1 = 8, Th2 = 2 → 8 ÷ 2 = 4 → In this example this would indicate a Strong tilt toward inflammation. but
Th1 = 2, Th2 = 8 → 2 ÷ 8 = 0.25 → This is indication of a Strong tilt toward anti-inflammation. But now consider that if Th1 = 5, Th2 = 5 → 5 ÷ 5 = 1 → Balanced immune state. What scientists refer to as a unity.
Here is a list of the cytokine protein ratios that were measured in this study
They measured the ratio between Interleukin 2 (pro-inflammatory) and Interleukin 10 (anti-inflammatory).
Between Interferon gamma (pro-inflammatory) and Interleukin 10 (anti-inflammatory)
Between Interleukin 2 (pro-inflammatory) and Interleukin 4 (anti-inflammatory)
Between Interferon gamma (pro-inflammatory) and Interleukin 4 (anti-inflammatory)
Between Interleukin 2 (pro-inflammatory) and Tumor necrosis factor alpha (pro-inflammatory)
And then finally they included the ratio between Interferon gamma (pro-inflammatory) and Tumor necrosis factor alpha (pro-inflammatory)
And if you notice what I noticed that the last two ratios were both pro-inflammatory. The simple explanation is that this gives a deeper look at what kind of inflammation is happening – not just how much. But I did decide to dig a little deeper.
When most of the pro-inflammatory cytokines are employed it can be said that they contribute to healthy immune activation and regulation, because inflammation is normal as it comes to the rescue when needed, it just needs not to grow into something chronic. Whereas, when TNF-α is in the picture it is known as dysregulating, harmful, and may be pathogenic. So, it’s not as simple as just evaluating a ratio where a pro-inflammation was compared to another pro-inflammation cytokine. It is the idea that if the result is a higher mathematical ratio, meaning the numerator is larger, this would indicate better immune regulation and less collateral damage to tissues. But a lower mathematical ratio, where the denominator is larger, specifically the TNF-α, means that inflammation may be running unchecked, with more destructive effects on the body, especially in a disease like Alzheimer’s.
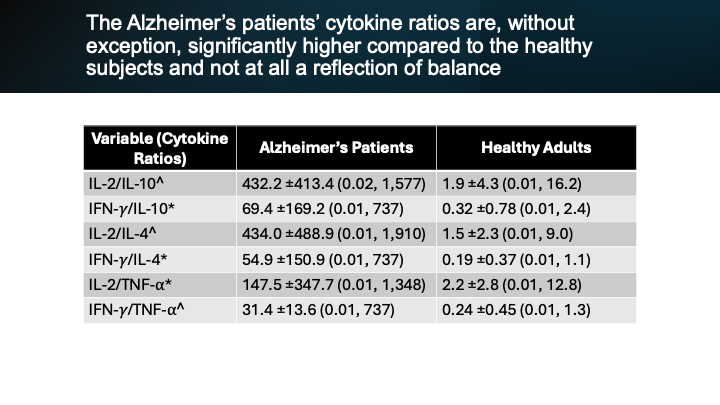
But the researchers did not just measure these cytokine ratios in Alzheimer’s patients. They first did so in healthy adults, 20 of them. These were the statistical results for these healthy adults. Their ratios were near unity for all values, meaning numerator (the top number above the forward slash) and denominator (the bottom number) are nearly equal, which would result in a quotient of 1, or in these cases “near 1”. Tapping high school math, any number divided by itself is equal to 1. But then they took 34 Alzheimer’s patients and measured these ratios in them, this is what they came up with. As you can see the Alzheimer’s patients’ cytokine ratios are, Without exception, significantly higher compared to the healthy subjects and not at all a reflection of balance. Take a minute and notice the differences. The researchers rated three of these ratios statistically significant. Indicated by the asterisk. And they rated the other three ratios as extremely significant indicated by the caret symbol. To say the least, the Th1/Th2 ratio is outrageously out of balance in these Alzheimer’s patients.
Before we look at the effects of the Aloe-Acemannan-based nutritional supplement on Alzheimer’s patients, it’s important to understand how their immune profiles compared to healthy adults. The study measured cytokine ratios (part of the immune system responses) and provided three key statistics for each group: the mean (average), the standard deviation (how spread out the numbers are), and the range (the lowest and highest values observed).
Let’s start with the healthy adults: This group represents the Control model against which we will compare the other results. I’ll focus on this first example as a way to explain further what this all means:
- Their average ratio was very low: 1.9. “near 1”
- The standard deviation was ±4.3, meaning the values didn’t vary much from the average.
- The full range of values went from 0.01 to 16.2. not a significantly wide range.
This shows that the immune responses in healthy individuals were tightly clustered, and that they had a balanced Th1/Th2 ratio—when all the cytokine ratios were calculated, what researchers sometimes call “near unity,” meaning close to 1. That’s a healthy sign. This signifies a statistical balance. This tells us that pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signals were in relative balance. And this was true of all six of the cytokine ratio statistics in the healthy adult group. All of them were near 1, All had relatively low standard deviations and all the lowest and highest values were not very far apart. This is indication that when pro-inflammation is needed it responds accordingly, but when anti-inflammation is needed it also responds accordingly. This is called balance or unity. It is also called healthy.
Now let’s look at the Alzheimer’s patients:
- In this example, the average ratio was 423.2, which is extremely high.
- The standard deviation in this example was ±413.4, which means the values were wildly spread out.
- The range in this example was 0.02 to 1,577, showing some patients had very low levels, and others had very high levels; a very substantial width in range
The rest of the stats reflected just more of the same no matter what cytokine ratio was tested. This wide variability tells us that the immune systems of Alzheimer’s patients were not balanced—specifically they leaned heavily toward inflammation, but in highly inconsistent ways from person to person. This makes the healthy group an important control model for comparison in the rest of the study.
The 34 people who participated in the study had moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s and each of them had been diagnosed for at least a year. They began their intake of APMC: Aloe Polymannose Multinutrient Complex. This same nutritional supplement was used two other studies we have curated at these links:
You can access these links in the transcription below. It’s main ingredient is Aloe Polymannose, which is Acemannan as well as rice bran, Flaxseed, Tart cherry, N-acetyl cysteine (an antioxidant), and other natural ingredients. They took four teaspoons each day for the next 12 months. Each teaspoon was equal to 2.5 grams of supplement powder.
The researchers determined that there was No serious side effects from APMC. Generally, No major safety concerns were found with the supplement.
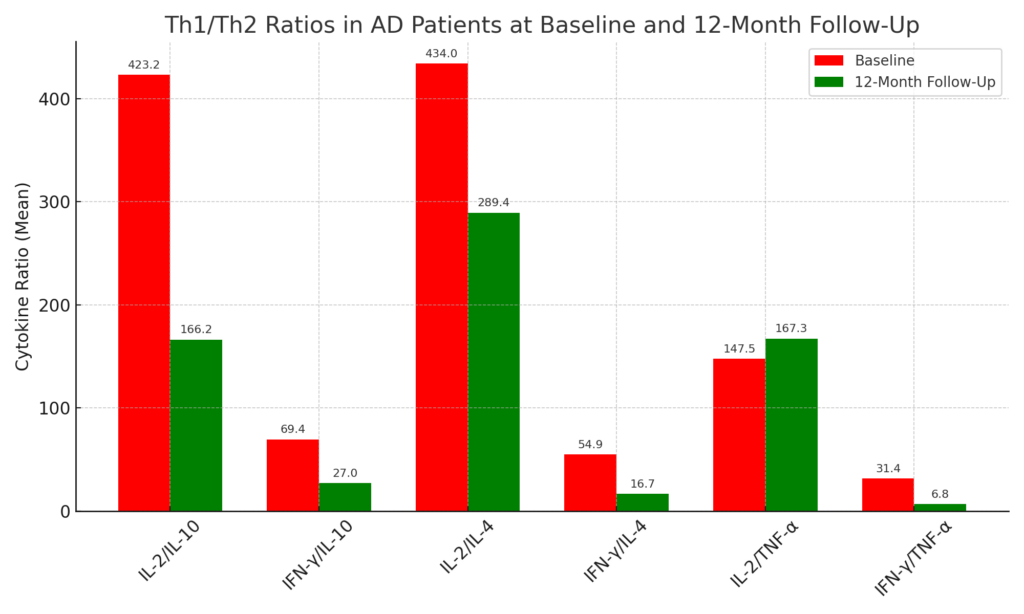
At the end of the 12 months they looked at the various ratios again. First, here is what was displayed earlier showing the measurements gleaned before they started the Aloe-Acemannan nutritional supplement. Then, here are the results they discovered at the end of the 12 months. Overall, the results were favorable. But let me elaborate.

The scientists identified two key dynamics to bring this research into plain view
What two dynamics am I talking about? These responsible researchers first addressed statistical certainty, which is revealed in 2 of 6 ratios, indicated by the asterisks and is also referenced as statistically significant. This is strictly mathematical using a method called F-statistic and p-value. The other 4 showed numerical changes, but they were not classified as statistically significant—meaning the changes, according to the math, could’ve been due to random chance.
However, the second thing the researchers did was to also interpret the same data in a broader context that was biological and clinical. Where 5 of the 6 ratios made movement in the right direction, indicated by the corresponding bar graph. The red bars represent the data reflecting the average before the experiment began and the green bars represent the averages at the end of 12 months of Alzheimers patients taking the Aloe-Acemannan nutritional supplement four times daily for 12 months. Five of the six green bars leaned in the right direction: less inflammation.
To summarize this section,“The numbers showed that two key inflammation markers improved significantly—but even beyond that, five out of six trended in the right direction. So while not every change hit the ‘official’ mark, the overall shift toward a healthier immune profile was clear—and it lined up with better memory scores, too.”
And speaking of memory scores, I did not mention earlier that at the beginning of the project they did a battery of 26 cognitive tests on the Alzheimer’s patients.
The Cognitive tests included ADAS, Alzheimers Disease Assessment Scale. This is a collection of tests to measure memory, language, and thinking skills.. The SIB Severe Impairment Battery. This is a series of tests that look at cognitive ability in people with advanced Alzheimer’s — especially memory and attention. The MMSE is the Mini-Mental State Examination. It evaluates General cognitive function — used to screen for memory problems and dementia. And the ADCS-ADL, the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study—Activities of Daily Living. This is a single test that tells How well someone can perform everyday tasks like dressing, eating, or bathing.
Here are the scores generated at the beginning of this project. We have the same format as the other Tables in the study. Average (mean), standard deviation, and range. Then we have the scores at the end of the 12 months, also in the same format.
- Higher scores on tests like MMSE, ADCS-ADL, and SIB mean better brain function.
- Lower scores on the ADAS scale generally mean improvement, except for one part called “Word Recognition Reminders.” With all that in mind, I have highlighted all the areas that reflect improvement
Final Conclusion: Alzheimer’s disease is growing fast, with serious impact on patients, families, and the healthcare system—and treatments haven’t made much progress. One thing we do know is that inflammation and an imbalanced immune system play a big role in this disease.
This study is the first to closely measure the Th1/Th2 immune ratio in Alzheimer’s patients, compare it to healthy people, and track how it changed after 12 months of taking an Aloe-Acemannan-based supplement. The results showed that these Alzheimer’s patients had very high Th1 (inflammatory) levels to start with. After a year of the Aloe-Acemannan, two of the six cytokine ratios made mathematical shifts with statistical significance toward better balance (more Th2), and clinically 5 of the 6 cytokine ratios moved in the right direction (also more Th2, less inflammation). Plus, their thinking and memory also improved in 6 out of 26 cognitive tests.
These results are promising, while more research is still needed to understand the full relationship between immune balance and brain health.
I hope you will always be careful to maintain good works to meet urgent needs and become heroes to your generation.